A big thank you to everyone who submitted an image in the 2019 Image Competition. We are excited to announce the winners. Please vote for these amazing images in the NNCI Image Contest, There’s Plenty of Beauty at the Bottom. Voting will open on October 7th!
Most Stunning
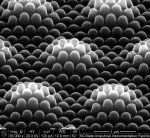
Gill raker of the Japanese medaka
Melissa Chernick, Duke University
This image shows a portion of a gill raker from a Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes), a small fish often used as a research model. Gill rakers are tooth-like structures inside a fish that help capture prey and prevent damage to its gills. The image shows some of the tissue that makes up the gill raker: a taste bud surrounded by pavement cells.
Most Unique Capability
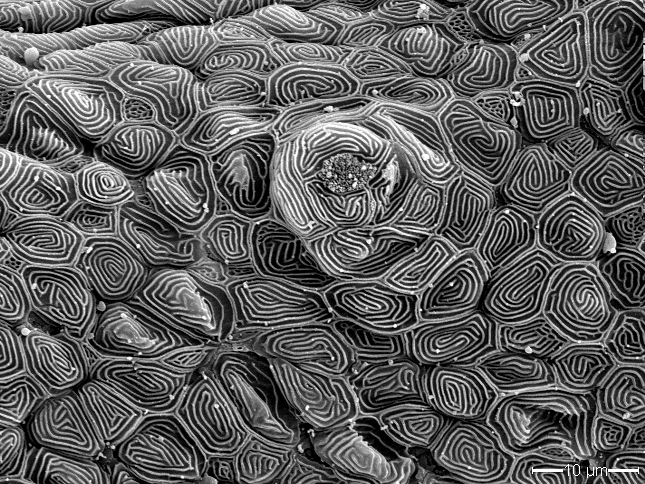
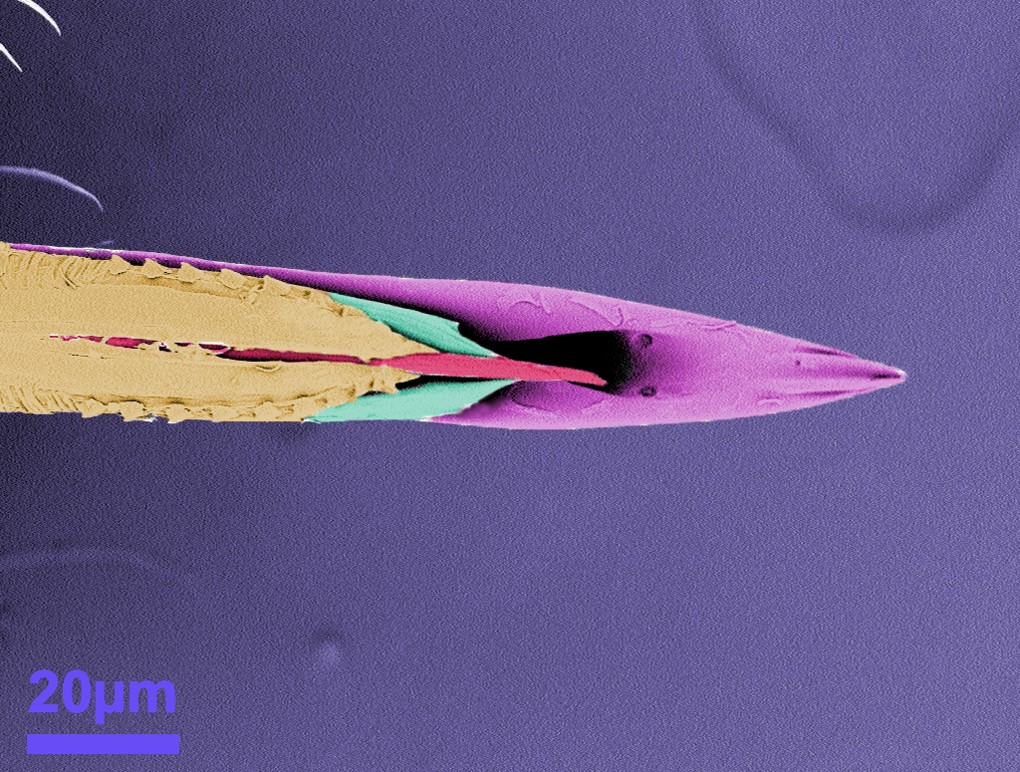
Nanocoined Structures in Diamond
Nichole Miller, Smart Material Solutions, Inc.
This image shows hierarchical features that were milled into diamond using a focused ion beam. This patented process, “Nanocoining,” can seamlessly nanopattern drum molds for roll-to-roll manufacturing hundreds of times faster than competing technologies. This enables nanopatterning that was previously feasible for only small, academic experiments to be applied on the industrial scale. Nanocoining opens the door for nanostructured surfaces with unique optical and wetting properties to be applied to a variety of commercial products including OLEDs, biosensors, wire-grid polarizers, solar panels, and windows.
Most Whimsical
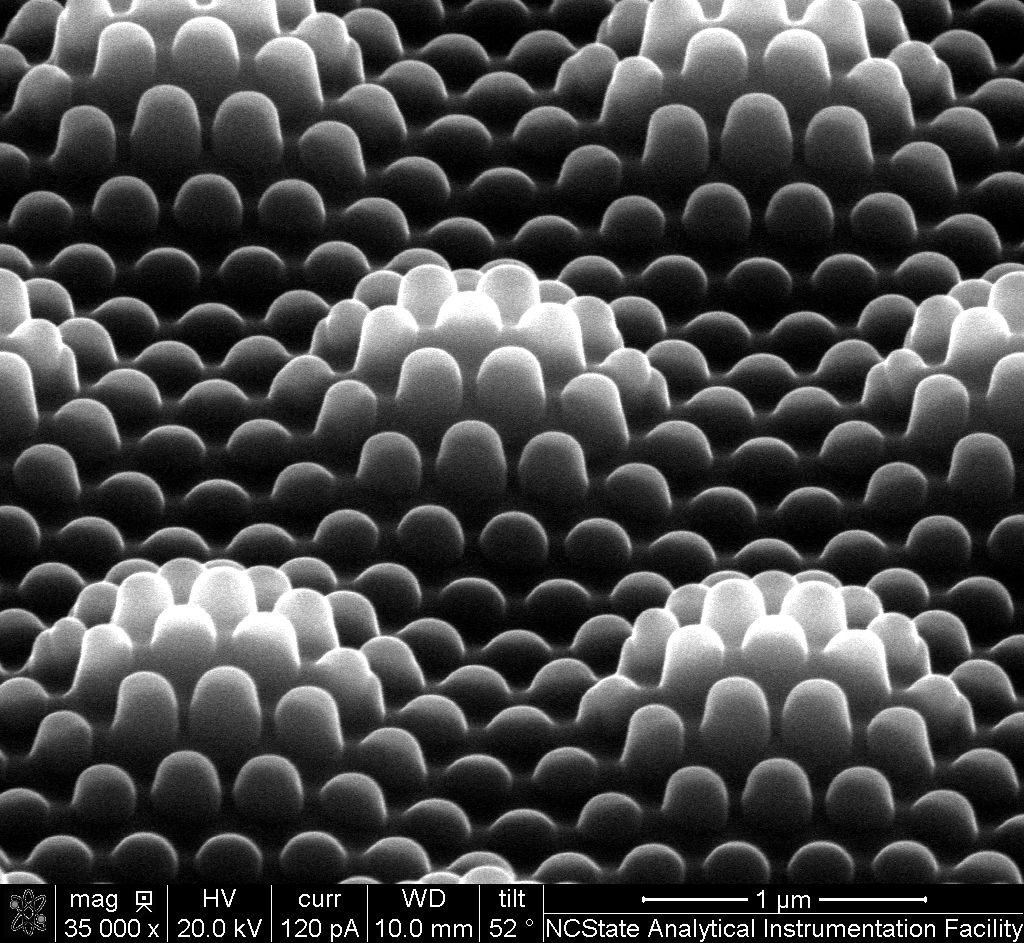
Dust Flower
Michael Valerino, Duke University
Particulate matter (PM) refers to liquid or solid particles suspended in the atmosphere and comes from dust, combustion by-products, exhaust, fires, and even vegetation. When PM deposits on the surface of solar panels, it can reduce energy production by up to 40% resulting in ~10 to 50 billion dollars of annual losses globally. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of particles on the panel surfaces help us to better understand the sources impacting soiling. This piece of dust reminded our group of a flower, seemingly blooming out of an unearthly field. Even at this tiny scale, we can find familiarity.